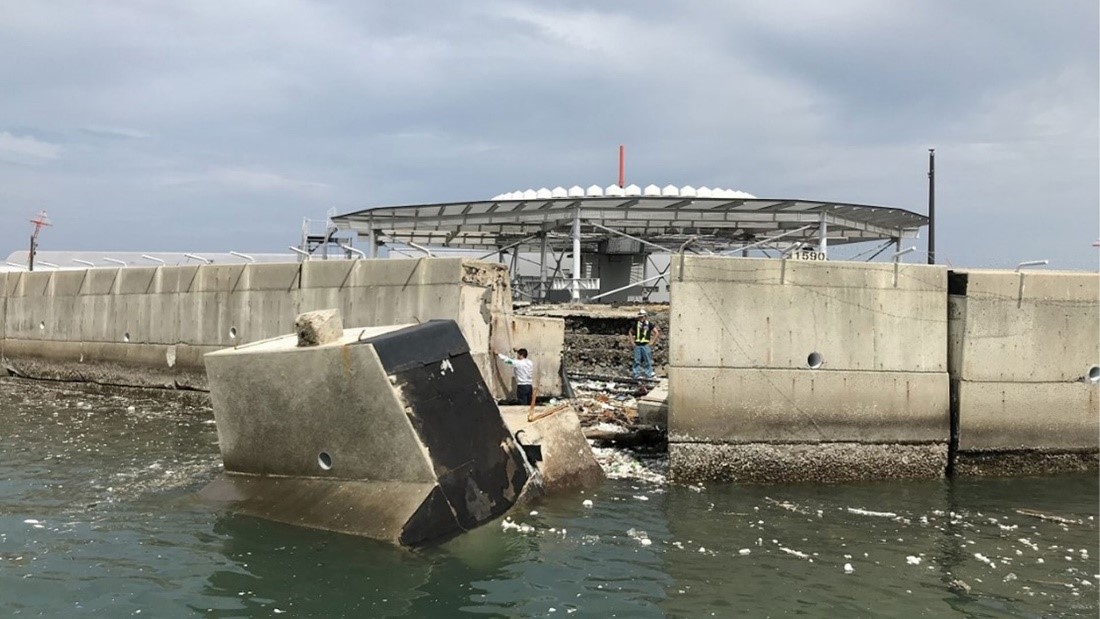
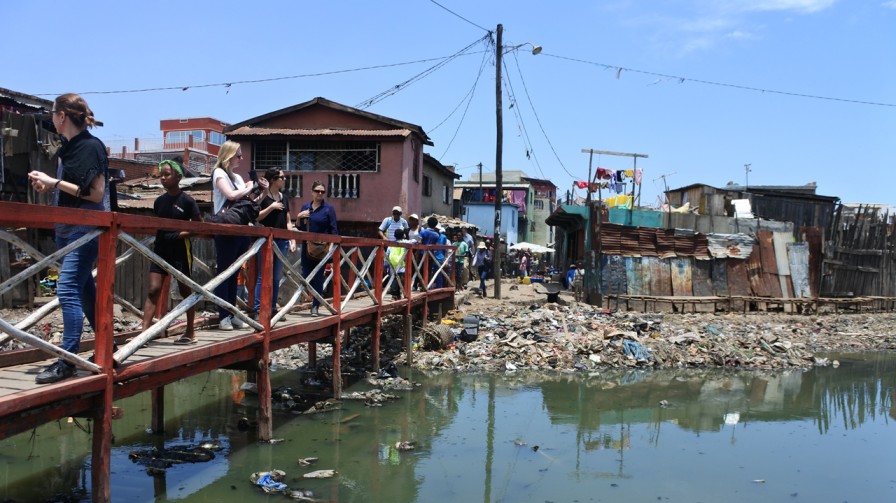
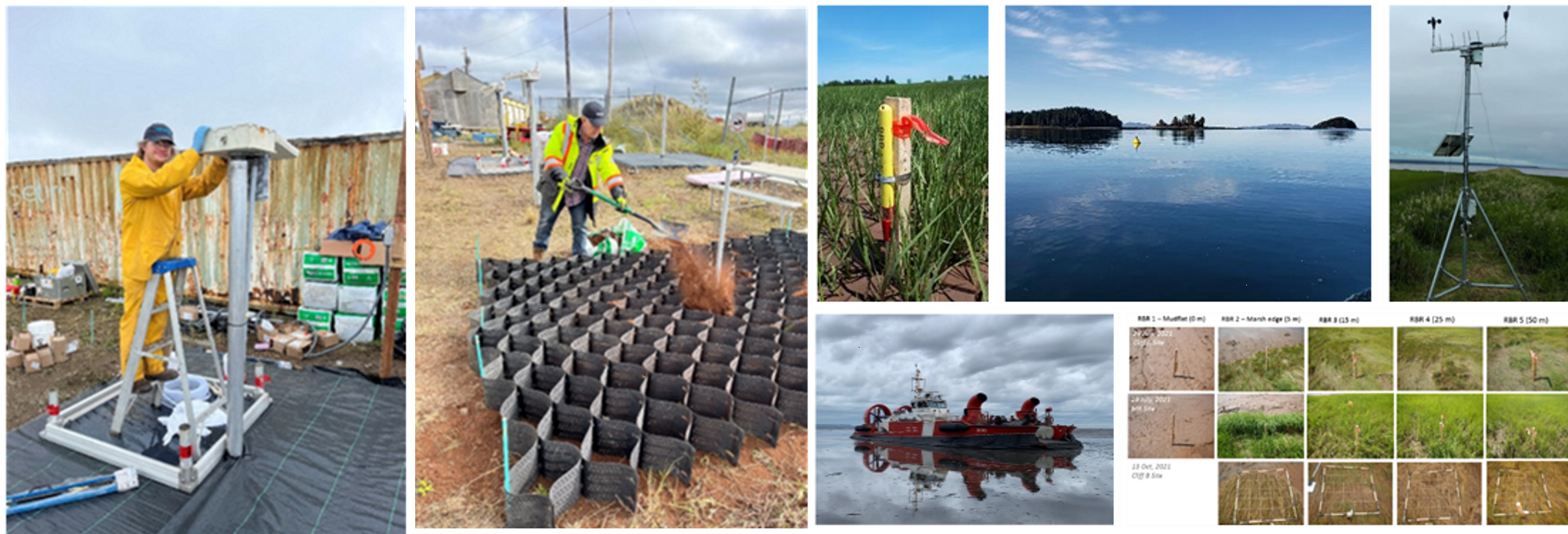
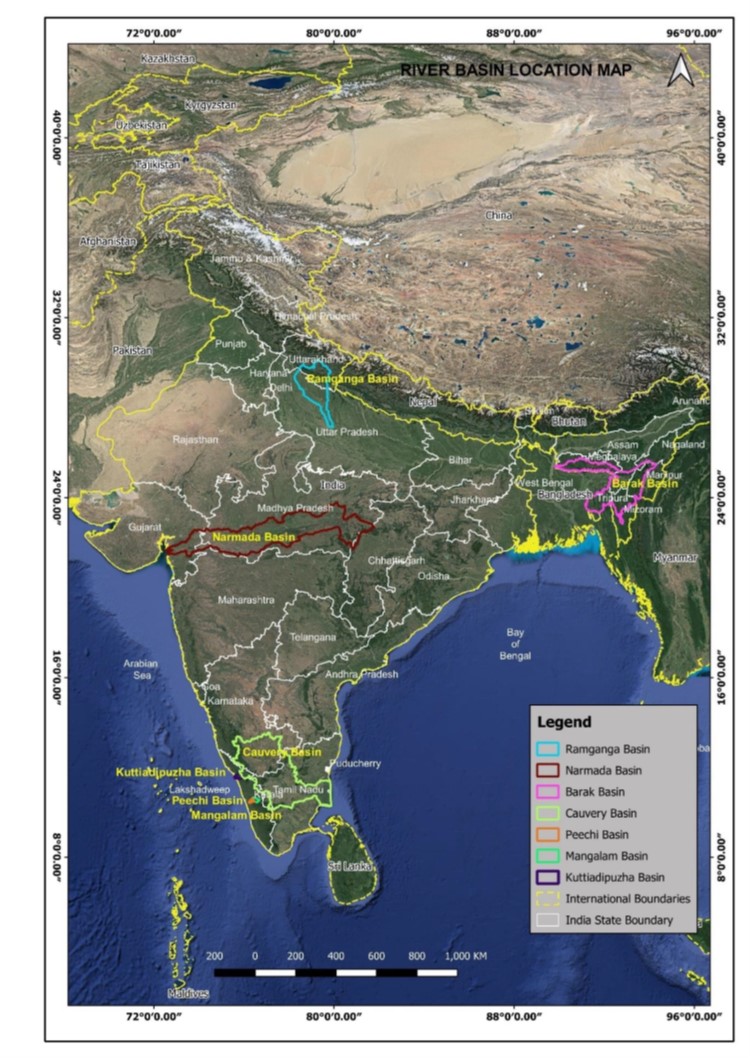
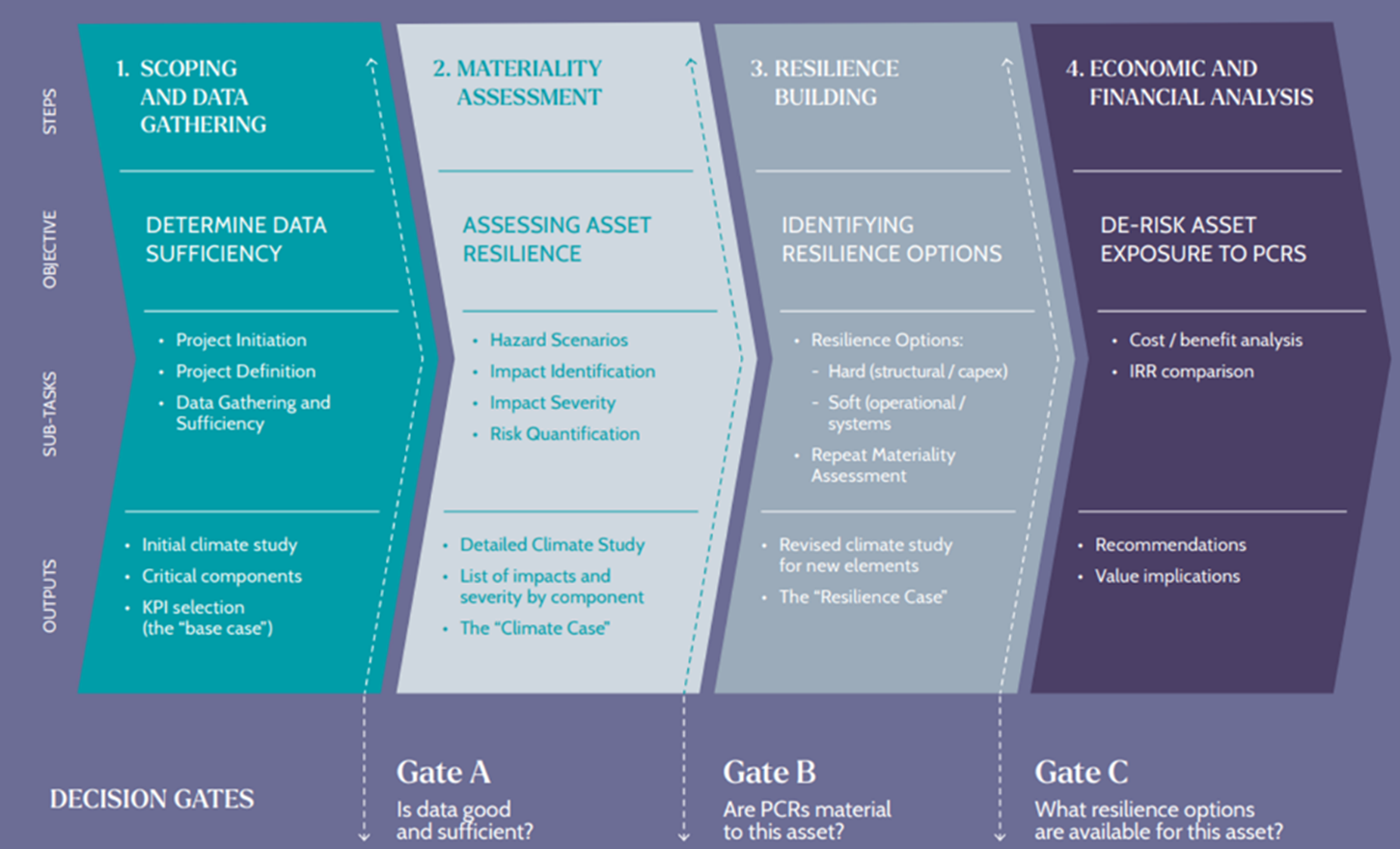
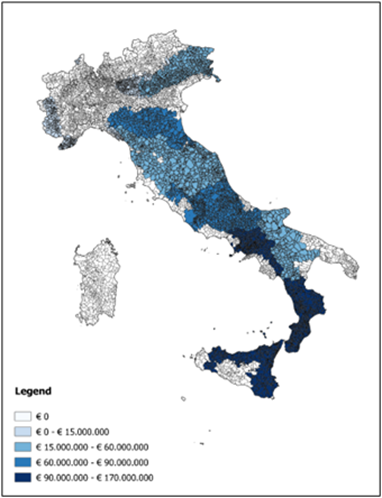
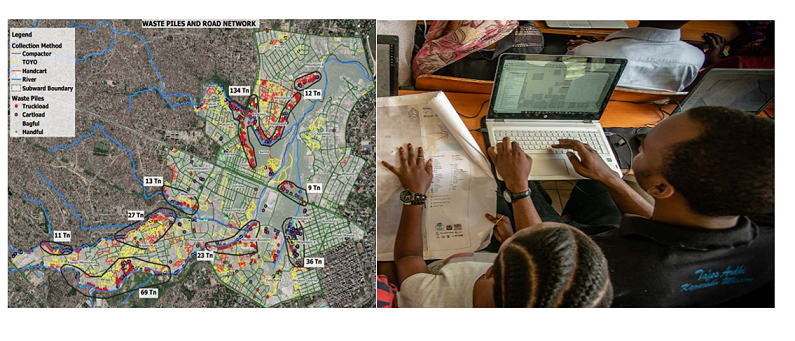
Thousands of Australians face bushfires, floods, and cyclones every year. It is known that for every dollar spent on disaster risk reduction, there is an estimated 9.60 AUD return on investment. The DRF is helping to curb the devastating impacts of natural hazards by investing in important disaster prevention projects. This includes direct investment in grey and green-blue infrastructure, for example flood levees, seawalls, and firebreaks.
Projects that target systemic risk reduction to build community resilience and capability were also eligible under Round One. Consultation with states, territories, local government, not-for-profit organizations, First Nations people, insurers and other key stakeholders will continue throughout the life of the DRF to ensure strong and constructive collaboration and the achievement of the maximum public benefit possible.
The DRF is given effect through the Disaster Ready Fund Act 2019. It directly contributes to Australia’s obligations under the UN Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 and Australia’s National Disaster Risk Reduction Framework. It is also supported by calls from industry and civil society, such as Insurance Council of Australia’s 2022 Building a more resilient Australia report, and the Climate Council and Emergency Leaders for Climate Action’s The Great Deluge: Australia’s New Era of Unnatural Disasters, which have both called for prioritised investment in resilience and adaptation.
Co-Benefits of the Initiative:
Projects under DRF Round One could target a broad range of natural hazards as outlined in the guidelines, and fall within either of the following categories:
Infrastructure projects, including:
- investment in grey infrastructure (ie. engineered assets such as levees or cyclone shelters)
- investment in green-blue infrastructure (including nature-based solutions)
- investment in hazard monitoring infrastructure; and/or
- business case development for future infrastructure (including investigation, modelling, concept, and detailed design activities). Projects in this stream could include flood levees, fire breaks, early warning systems and planning to reduce risk.
Systemic risk reduction projects, including:
- supporting a better understanding of risk, through a better evidence base to understand and raise awareness of risk
- strengthening decision making by enhancing effectiveness of governance networks and communities of practice
- adaptation projects that improve land use planning and development practice projects
- projects that build the capacity and capability of businesses, community organizations and/or at-risk communities to improve their preparedness and resilience to the impacts of future disasters; and/or
- projects that enable and incentivize private investment in disaster risk reduction.
Projects in this stream could include jurisdiction-wide hazard-based information systems, updating resilience strategies and hazard research.
Round One of the DRF was generally well received by states and territories, and local communities, and feedback from key stakeholders has been largely positive. Some of the main challenges noted by stakeholders included securing matching funding and meeting the timeframes. Round One guideline was released in January 2023 and applications closed in March 2023. Applicants could request a waiver of the co-contribution requirement if they could demonstrate rare and exceptional circumstances. NEMA also received feedback regarding the application process, which involved lodgment through states and territories using an online form developed by NEMA, and the administrative burden on states and territories.
Scalability:
Round Two (and future rounds) of the DRF provides an opportunity to address the practical challenges identified through Round One, as well as to consider how the strategic intent of the program can be strengthened. Consultations with key stakeholders will consider these issues as Round Two is designed.